Google’s March Update: What You Need to Know
By Sam Singleton
- Improved quality ranking: Algorithmic enhancements to core ranking system, ensuring that the most helpful information surfaces on the web and reduces unoriginal content appearing in search results.
- New and improved spam policies: Google is updating their spam policies to keep the lowest-quality content out of search, including expired websites repurposed as spam repositories by new owners and obituary spam.
Google’s latest core update launched earlier this month, and based on the chatter within the community and from Google themselves, it’s fair to say that this is a big one. Many have even gone as far to say that it could be as significant as the hummingbird or panda update.
In 2022, Google started tuning its ranking systems in an effort to reduce unhelpful and unoriginal content on search. The 2024 update appears to be an extension of the work previously done, with Google stating in an announcement that the learnings from this work are being brought into the latest update.
Further reinforcing the significance of this update, Google expects that the combination of this, paired with their efforts in 2022, will cut down the presence of low-quality, unoriginal content in search results by as much as 40%.
Essentially, this latest Google update is aimed squarely at the following 2 problems:
- Deindexing of Low-Quality, AI-Generated Content & Spam sites
- Changes to Link Signals
Our own SEO Director, Alex Whalley ran a number of tests with small ‘dropshipping sites’ to gauge the impact of not only low quality content, but also of the impact of building a backlink profile made up of spammy links originating from known link farms, PBNs (Private Blog Networks) and large scale directory listing backlinks.
The results are interesting to say the least, and not only do they confirm what Google has been saying about the deindexing of low quality, AI generated content and spam sites, they also give us a glimpse into how you can still rank well with AI Generated content when you follow the rules and ensure SEO best practices are being adopted throughout other aspects of the site.
- Deindexing of Low-Quality, AI-Generated Content and Spam sites:
Alex and his team at Tug Sydney noticed that
“A substantial number of websites have been deindexed for relying heavily on AI-generated content and failing to offer high-quality, human-generated content that addressed real problems or provided unique and relevant solutions”.
Many of you may be reading this and starting to panic, thinking ‘but I have already utilised AI Generated content, and some of my backlinks are questionable at best!’
So is there a way to undo this penalty and ‘absolve your site’ in the eyes of Google?
The team ran a test with a luxury watch dropshipping site that was only a few months old and had a domain authority of around 8, a score that had been accumulated through the creation of unique content, an SEO friendly product hierarchy, related FAQ content and around 20-30 backlinks built using guest posting and proper outreaching processes to related websites. It went a little something like this:
Day 1 – Link Acquisition:
- We ordered 1000 directory listing links from a seller on the Fiverr platform
- We ordered 100 Web 2.0 sites to be built, using 1 piece of Ai Generated content that would then be rewritten 100 times for each web 2.0 site (sites like Wix, Blogger etc)
- We ordered a 10 guest post package and paid extra to have the content generated
Day 2 – Publishing 10 new AI Generated articles:
- We asked ChatCPT to come up with 10 article ideas around the Luxury Watch market. Our prompts were deliberately limited to that exact phrasing.
- We scheduled these 10 articles to publish 2 per day on the blog for a 5 day period.
The results
After an additional 7 days when all links had been delivered and all articles had been published we checked the domain rating and indexing of these pages in Ahrefs and Search Console. The domain rating in Ahrefs had fallen from 8 to 3 – a loss of 5 DR points representing a 62.5% drop in authority.
We also noticed that the number of ranking keywords for the site had dropped significantly, with around 100 less search queries listed in Google Search Console.
Undoing the Damage…
Over the next few weeks we focused on generating useful content that addressed customer pain points, seasonality, product-centric tips and guides, and FAQs that aligned with ‘People Also Ask’ questions as found in the search results. We still used ChatGPT to generate this content but ensured that we would then rewrite and update at least 50% of the resulting content, adding contextual links to relevant sources, as well as internal links to related products and pages across the site.
We then actively started outreaching with some of this helpful content and acquired relevant quality links to this content. We also actively participated in guest posting, sharing some of this unique content with other webmasters in order to acquire even more backlinks.
We checked back after just over two weeks, and the results speak for themselves…
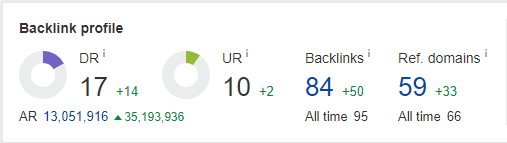
The site, which originally had a DR of 8 and had dropped down to 3 now has a Domain Rating (DR) of 17 – an increase of 14 authority points. This has resulted in a surge in clicks and impressions to the site, as well as the total number of queries that are driving these clicks and impressions.
The Takeaway
It’s not too late to fix what is broken. Whilst Google is penalising sites that have heavily relied on AI generated content and spammy links to grow their search engine visibility, changing how you do things can bring you back again.
Just remember that content should be written for users first and search engines second, and while you can still rely on AI to help come up with content ideas and overall frameworks, you still need to do your research, understand your audience, and most importantly – write and/or edit your content so that it actually adds value.
- Changes to Link Signals:
The Core Update has also introduced four significant changes to how link signals are interpreted within its ranking algorithm. These changes aim to refine the evaluation of links to prioritise content quality and deter link manipulation strategies. Let’s take a deeper look into each of these changes:
- De-emphasising Links as a Ranking Signal: One of the notable adjustments is the apparent de-emphasis of links as a crucial ranking signal. Previous documentation highlighted links as an “important” factor in determining the relevance of web pages. However, the updated guidance modifies this stance, simply stating that links are a factor, without the emphasis on their importance. This change aligns with comments from Google representatives, indicating a shift away from prioritising links above other quality indicators in the ranking process.
- Content Created for Link Manipulation: The update also addresses the creation of content primarily for the sake of manipulating linking and ranking signals. This refers to the practice of generating low-value content with the main objective of influencing link-based metrics. Google’s adjustment suggests a move to penalise or reduce the impact of such content, marking a step against the manipulative use of content to game the ranking system.
- Outgoing Links as a Signal: Another area of focus is on manipulative outgoing links. Google has traditionally penalised sites that sell links or engage in link schemes designed to manipulate PageRank. The update brings attention to outgoing links from a site as a factor for scrutiny, implying that Google’s algorithm now more actively considers how sites link out to others as part of its evaluation of link spam.
- Expired Domains Signal: Lastly, the update brings in a new consideration for expired domains. The use of expired domains as a tactic to inherit authority and manipulate rankings has been a grey area in SEO. The update suggests that Google is taking a stronger stance against the use of expired domains for SEO advantage, potentially penalising or devaluing links from such domains.
Together, these changes represent a comprehensive update to Google’s approach to evaluating link signals, emphasising the quality and relevance of content over the quantity and manipulation of links. The shift indicates Google’s ongoing efforts to reward genuine, high-quality content that serves user intent, while penalising practices that attempt to manipulate search rankings through link schemes and low-value content.
The overall emphasis of the March 2024 update is clear: Google seeks to promote originality, depth, and value for the reader, with a stronger stance against manipulative SEO practices and low-quality content. Adapting to these changes is essential for maintaining or improving your site’s visibility in search results.
The team at Tug Sydney were also able to show how, with the right SEO knowledge and an understanding of the importance of addressing customer queries with relevant and useful information, sites that may have a lot of AI generated content and ‘questionable’ links in their existing backlink profile can still escape the wrath of Google’s latest algorithm update’ and bring themselves back onto the first page of the SERPs.


