Internal Linking – Why Is It Important And What To Consider
Internal linking can be a complicated matter, yet the concept is pretty simple. Undoubtedly, it is a very important and powerful technique to boost a website’s performance. However, many websites don’t get this quite right and it can be easily one of the most overlooked factors in SEO optimisation. This short guide will discuss why having an optimised internal linking strategy is important for any website – no matter what size – and how to get started.
But let’s start with a short definition of internal links…
“Internal linking refers to any links from one page on a domain which lead to another page on that same domain.”
An internal link can sit anywhere on a website and point to another page on the same website, however, the most common form of internal linking is having links point from the main site navigation to a sub-category within the website. Other common areas to feature internal links include side bars, footers and links within articles.
Why are internal links so important?
These type of links are useful for various reasons:
- They allow users to navigate a website and provides the audience with further reading options. This may reduce bounce rate & at the same time trigger increased user engagement.
- They help establish information hierarchy for the given website and thus, strengthen the website’s architecture.
- They help spread link juice (ranking power) around websites and can help improve rankings for certain keywords.
- They can help to promote events and other paid services on a website.
Apart from helping search engine spiders discover all pages within a website and thus, strengthen the website’s navigational structure and architecture, internal links also provide a better user experience and help readers discover more interesting content on a website.
How does it work?
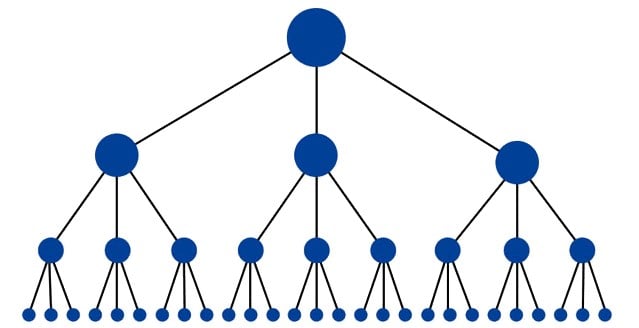
The optimal structure for a website should look similar to a pyramid (with the homepage on top):
Linking the homepage to any given page on a website, helps passing linking juice (ranking power) through the whole site and increase the ranking potential for each individual page.
Who does it well?
The above structure is very common and many large ecommerce sites, such as Amazon, Ebay and Asos do this really well.
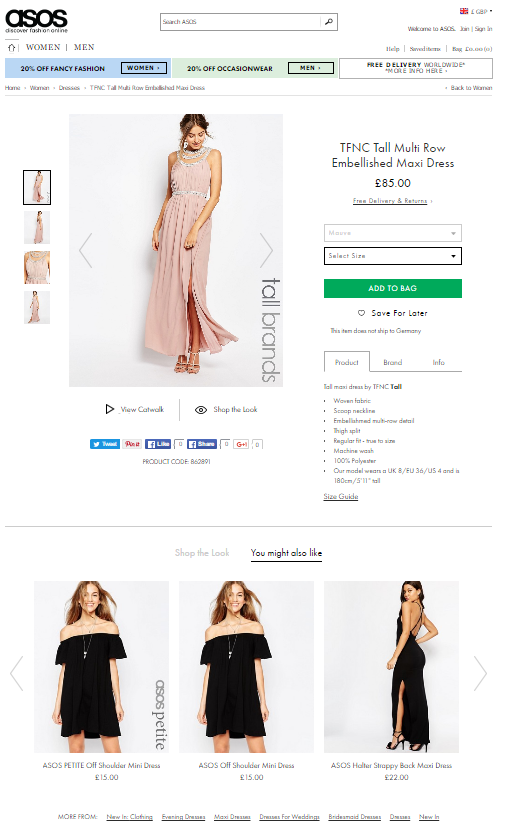
Here’s the example of Asos:
Asos product pages provide users with links to related products and other products the user might like. In addition to this, more buying information on the chosen product is given on the page. This will give the user many opportunities to click further through the site and hence, more incentives to buy additional products, and at the same time increase user behaviour metrics and engagement.
Top 10 tips to get started with internal linking
- Identify where a review is needed – use Screaming Frog and Google Search Console to identify which pages need some help from internal linking and which pages are getting more attention than they are worth.
- Before you add an internal link, ask yourself: „How likely is it that a user will click on this link?“ – The higher the probability, the more juice this link will pass and the more value this link will have from an SEO point of view.
- Choose your anchor text wisely – ensure it is very closely related to the topic of the landing page. This is particularly important for internal links in articles as search engines are getting pretty clever at making sense of a large amount of text! Links within content typically pass greater value because they are surrounded by contextual words which can have another benefit in terms of ranking for these related phrases.
- Choose the position of the link on the page – ideally within the first few sentences of a blog post/ above the fold.
- Ensure internal links are followed – There is no reason why they shouldn’t!
- Ensure relevancy and context – ensure that internal links appear to be natural and not manufactured.
- On the homepage, add links to the most important pages – e.g. product pages or main categories.
- Any new pieces of content should include relevant links to other important landing pages – This will ensure that any links you build to your content will also have a secondary benefit on the pages you’ve internally linked to.
- Add internal links in moderation – generally, 2 internal and 1 external links are recommended in a standard article of around 700 words. Don’t exceed 100-150 internal links per page.
- Make sure links add value – SEO is a factor of course, but links should also add value to the reader, perhaps pointing to an in-depth look at a topic which was only briefly mentioned in an article, or pointing users at some relevant statistics.